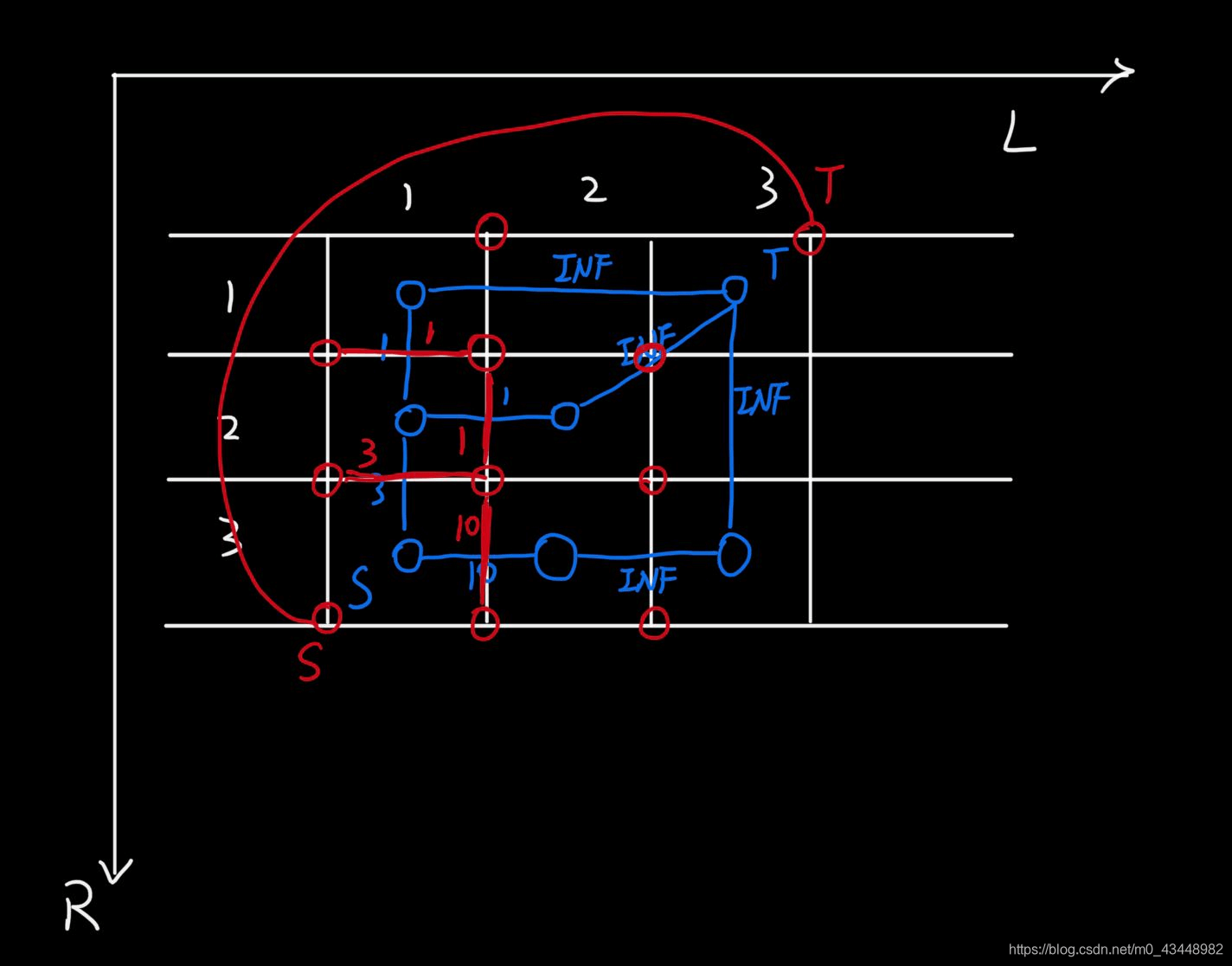
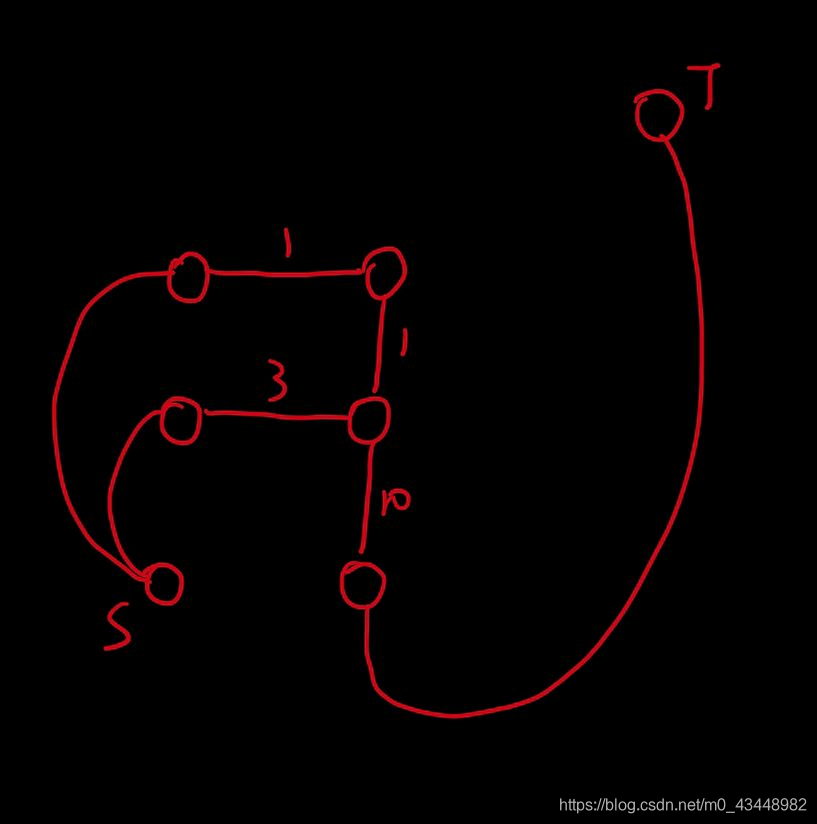
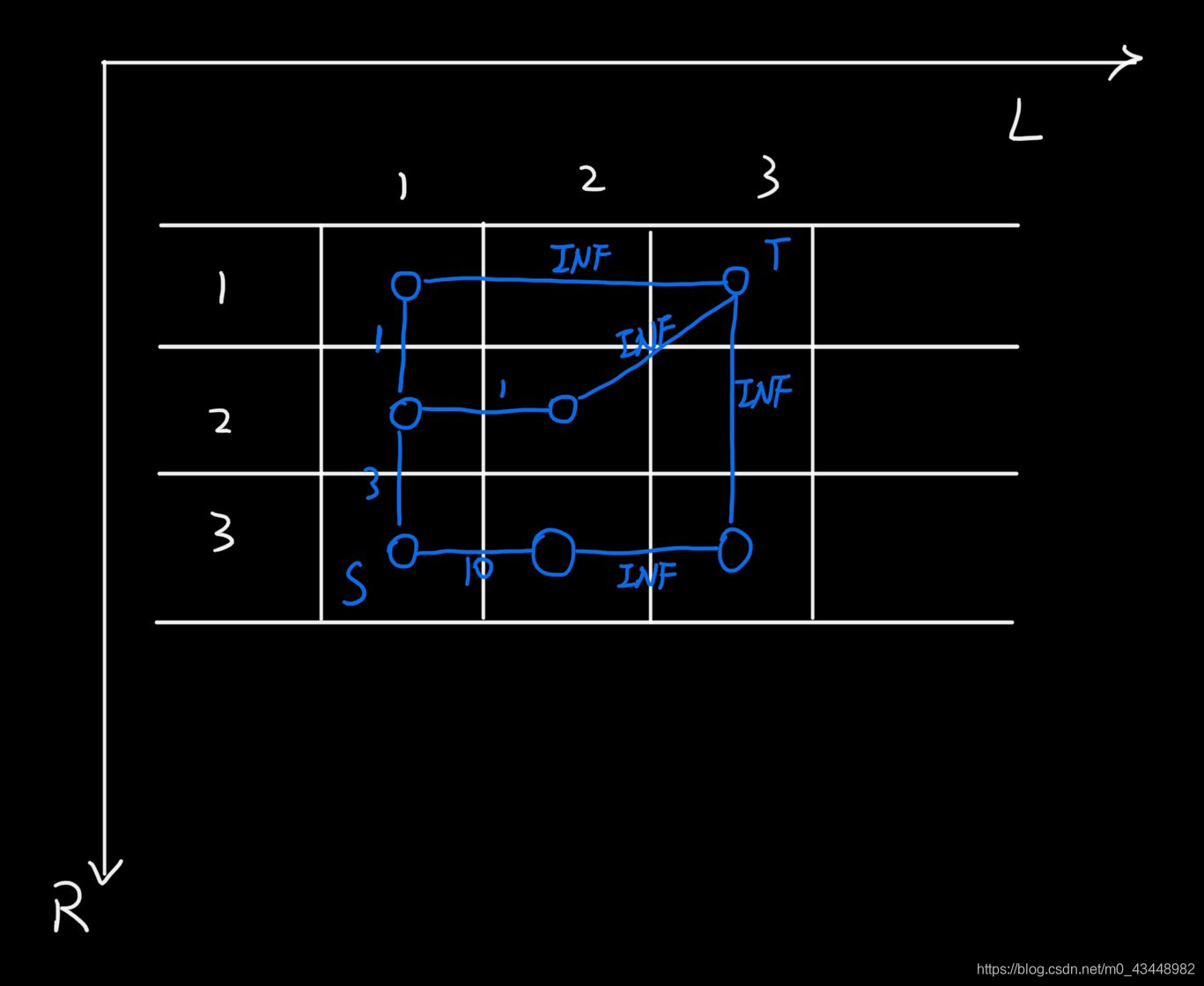1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int maxn = 510;
int n, m;
ll dis[maxn * maxn];
char si;
vector<pair<ll, int>> G[maxn * maxn];
void addedge(int u, int v, int cost) {
G[u].push_back({cost, v});
}
ll dijkstra(int s, int t) {
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
dis[s] = 0;
priority_queue<pair<ll, int>, vector<pair<ll, int>>, greater<pair<ll, int>>> q;
q.push({0ll, s});
while (!q.empty()) {
ll u = q.top().second, c = q.top().first;
q.pop();
if (dis[u] < c)continue;
for (auto i : G[u]) {
ll cc = i.first, v = i.second;
if (dis[v] > dis[u] + cc) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + cc;
q.push({dis[v], v});
}
}
}
return dis[t];
}
inline int id(int x, int y) {
return x * (n + 3) + y;
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int u, v, w;
char c;
cin >> u >> v >> c >> w;
if (c == 'L') {
addedge(id(u, v), id(u, v + 1), w);
addedge(id(u, v + 1), id(u, v), w);
} else {
addedge(id(u, v), id(u - 1, v), w);
addedge(id(u - 1, v), id(u, v), w);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
addedge(id(0, 0), id(0, i), 0);
addedge(id(i, n + 1), id(n + 1, n + 1), 0);
}
dijkstra(id(0, 0), id(n + 1, n + 1));
if (dis[id(n + 1, n + 1)] >= 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f)
cout << -1 << endl;
else
cout << dis[id(n + 1, n + 1)] << endl;
}
signed main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
#ifdef ACM_LOCAL
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
int test_index_for_debug = 1;
char acm_local_for_debug;
while (cin >> acm_local_for_debug) {
if (acm_local_for_debug == '$') exit(0);
cin.putback(acm_local_for_debug);
if (test_index_for_debug > 20) {
throw runtime_error("Check the stdin!!!");
}
auto start_clock_for_debug = clock();
solve();
auto end_clock_for_debug = clock();
cout << "Test " << test_index_for_debug << " successful" << endl;
cerr << "Test " << test_index_for_debug++ << " Run Time: "
<< double(end_clock_for_debug - start_clock_for_debug) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl;
cout << "--------------------------------------------------" << endl;
}
#else
solve();
#endif
return 0;
}
|